Power distribution cabinets play a critical role in modern electrical infrastructure, serving as the interface between high-voltage transmission lines and low-voltage end-use applications. At the heart of these cabinets are the latches, which secure the doors and provide both functional and safety-related benefits. This article delves into the key aspects of high and low voltage power distribution cabinet latches, exploring their design, functionality, and importance in ensuring reliable and secure power delivery.
The Importance of Power Distribution Cabinets
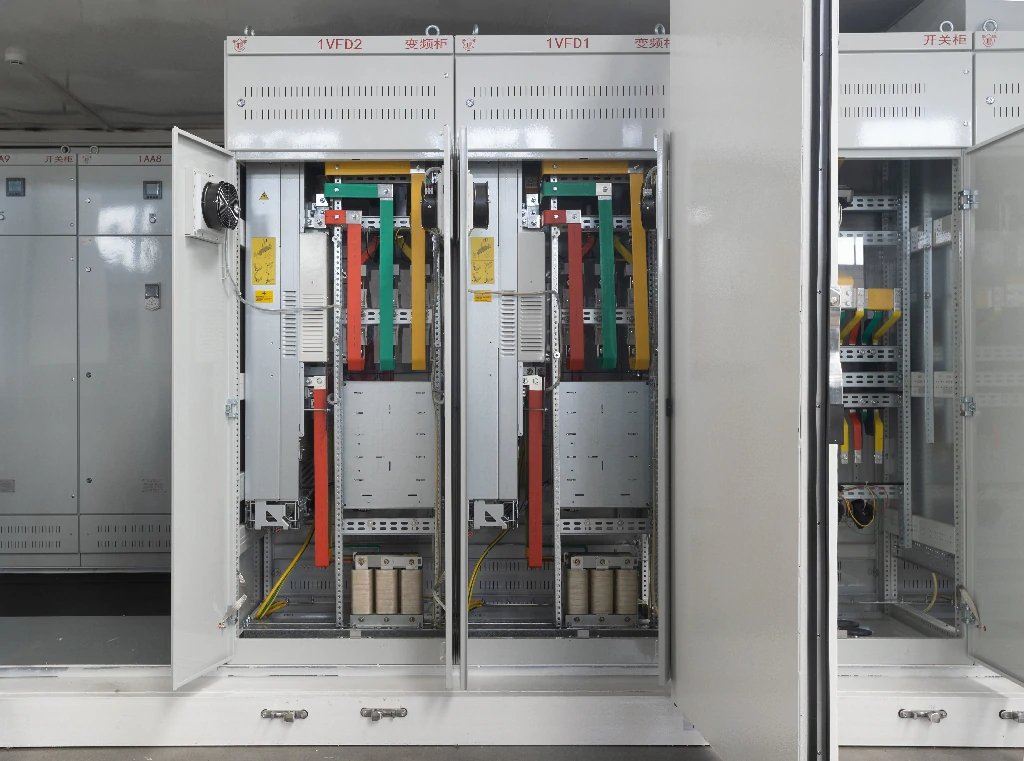
Power distribution cabinets are the backbone of electrical systems, responsible for transforming and distributing electricity from high-voltage transmission networks to lower-voltage applications, such as homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. These cabinets house the necessary equipment, including transformers, circuit breakers, and other essential components, to safely and efficiently manage the flow of electricity.
The proper functioning of power distribution cabinets is paramount to the overall reliability and stability of the electrical grid. Disruptions or failures in these cabinets can lead to widespread power outages, with significant economic and societal consequences. As such, the design and construction of these cabinets, including the latches that secure their doors, must adhere to rigorous safety and performance standards.
The Role of Latches in Power Distribution Cabinets
Latches play a crucial role in power distribution cabinets, serving several important functions:
- Door Security: Latches ensure that the cabinet doors remain securely closed, preventing unauthorized access and potential tampering with the sensitive electrical equipment inside.
- Seguridad: Latches act as a barrier, preventing accidental or unintended opening of the cabinet doors, which could expose personnel to the high-voltage components within, posing a significant safety risk.
- Environmental Protection: Properly designed latches help maintain the cabinet's environmental integrity, shielding the internal components from the elements, such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures, which could compromise the cabinet's functionality.
- Conformidad: Latches in power distribution cabinets must adhere to industry standards and regulations, such as those set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), to ensure the overall safety and reliability of the electrical system.
High Voltage vs. Low Voltage Latches
Power distribution cabinets can be broadly categorized into two main voltage ranges: high voltage (typically above 600 volts) and low voltage (typically below 600 volts). While the core function of the latches remains the same, the specific design and engineering considerations differ between these two voltage ranges.
High Voltage Latches
High voltage power distribution cabinets require latches that can withstand the increased electrical stresses and potential arc flash hazards associated with the higher voltages. These latches must be designed with the following key considerations:
- Insulation and Dielectric Strength: High voltage latches must have superior insulation properties and dielectric strength to prevent electrical arcing and maintain the cabinet's overall safety.
- Mechanical Robustness: The latches must be able to withstand the increased mechanical stresses and vibrations that can occur in high voltage environments, ensuring reliable and long-lasting performance.
- Arc Flash Protection: High voltage latches may incorporate specialized features, such as arc flash barriers or current-limiting mechanisms, to mitigate the risks associated with potential arc flash events.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: High voltage latches must adhere to stringent safety standards, such as those set by the IEC, to ensure the overall safety and reliability of the power distribution system.
Low Voltage Latches
While low voltage power distribution cabinets still require robust and secure latches, the design considerations are generally less stringent compared to their high voltage counterparts. Key considerations for low voltage latches include:
- Facilidad de uso: Low voltage latches may prioritize user-friendly features, such as ergonomic handles or single-handed operation, to facilitate easier access and maintenance.
- Relación coste-eficacia: Low voltage cabinets often have tighter budgetary constraints, so the latches must balance performance and safety with cost-effective manufacturing and installation.
- Resistencia medioambiental: Low voltage latches may still need to provide a degree of environmental protection, such as resistance to moisture, dust, and corrosion, to ensure reliable operation in diverse installation environments.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Low voltage latches must still adhere to relevant safety standards, such as those set by NEMA, to ensure the overall safety and reliability of the power distribution system.
Design Considerations for Power Distribution Cabinet Latches
Regardless of the voltage range, power distribution cabinet latches must be designed with a range of factors in mind to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Some of the key design considerations include:
- Durability and Strength: Latches must be engineered to withstand the physical stresses and environmental conditions they will encounter during their lifetime, including repeated opening and closing, vibrations, and exposure to various weather elements.
- Ease of Operation: Latches should be designed with user-friendly features, such as ergonomic handles or mechanical assistance, to facilitate simple and efficient door opening and closing, even for personnel wearing personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Mecanismos de bloqueo: Latches may incorporate advanced locking mechanisms, such as keyed locks or electronic access controls, to enhance security and restrict unauthorized access to the cabinet's contents.
- Tamper-Resistance: Latches should be designed to resist attempts at unauthorized access or tampering, deterring vandalism or malicious acts that could compromise the cabinet's integrity.
- Environmental Protection: Latches must be engineered to provide a robust seal against environmental factors, such as moisture, dust, and corrosive agents, to maintain the cabinet's internal environment and protect the sensitive electrical components.
- Cumplimiento de las normas: Latches must adhere to the relevant industry standards and regulations, ensuring they meet the necessary safety, performance, and certification requirements for power distribution cabinets.
Conclusión
Power distribution cabinets are essential components of modern electrical infrastructure, and the latches that secure their doors play a critical role in ensuring the overall safety, reliability, and functionality of these systems. Whether in high voltage or low voltage applications, the design and engineering of power distribution cabinet latches must balance a range of factors, including security, safety, ease of use, and environmental protection.
By understanding the importance of these latches and the specific design considerations for high and low voltage applications, electrical engineers, manufacturers, and maintenance professionals can work to improve the performance and resilience of power distribution systems, ultimately contributing to the overall stability and efficiency of the electrical grid.