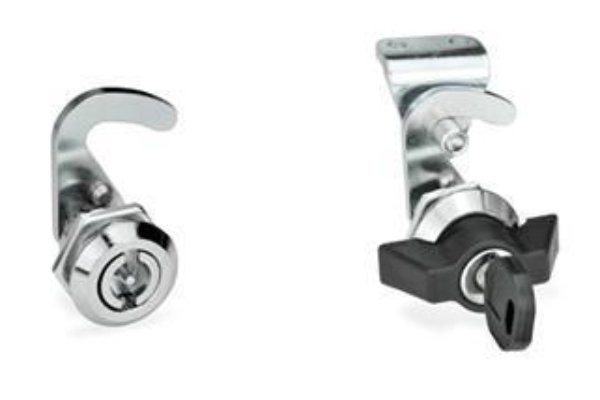
Electric cabinets are critical components in various industries, housing essential electrical equipment such as circuit breakers, controllers, and other devices. Securing these cabinets is vital to prevent unauthorized access and protect valuable assets. This guide provides an in-depth look at the main types of access restriction methods available for electric cabinets, their applications, benefits, and considerations for buyers.
Understanding Access Restriction Methods
Access restriction methods are security measures designed to control who can access the contents of electric cabinets. Selecting the right method depends on several factors, including the level of security required, the environment in which the cabinet is located, and user accessibility needs. Below are the primary access restriction methods used in electric cabinets.
1. Key Locking Mechanisms
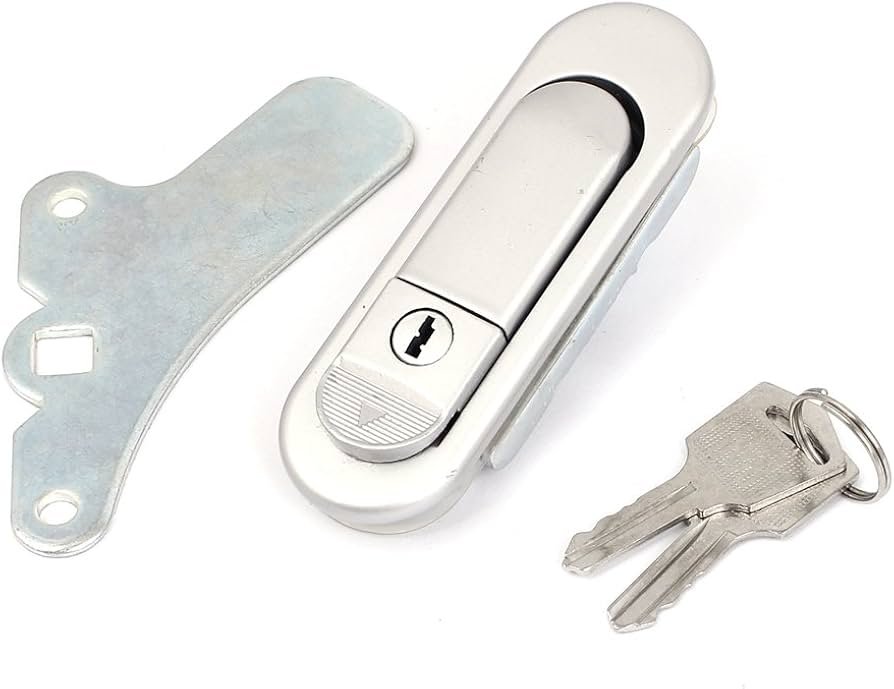

Overview: Key locking mechanisms are traditional locks that require a physical key to operate. They are widely used due to their simplicity and reliability
Sovellukset:
- Industrial Settings: Often found in factories where quick access is needed without complex systems.
- Residential Use: Common in home electrical panels to restrict access to children or unauthorized individuals.
Ominaisuudet:
- Mechanical Operation: No electronic components involved.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than electronic alternatives.
Benefits:
- Simplicity: Easy to install and use.
- Luotettavuus: Functions without needing batteries or power sources.
Considerations:
- Avainten hallinta: Keys can be lost or duplicated, leading to potential security risks.
- Limited Access Control: Changing who has access can be cumbersome, especially in larger organizations.
2. Electronic Access Control

Overview: Electronic access control systems utilize technology such as keypads, RFID readers, or biometric scanners to manage access to cabinets.
Sovellukset:
- Corporate Offices: Used in office environments to restrict access to sensitive areas like server rooms.
- Healthcare Facilities: Protects pharmaceuticals and medical equipment by restricting access to authorized personnel only.
- Educational Institutions: Controls entry into laboratories or storage areas containing hazardous materials.
Types of Electronic Access Control:
- Keypad Locks: Require users to enter a code for entry.
- RFID Locks: Use RFID cards or fobs for authentication.
- Biometric Locks: Employ fingerprint or iris recognition for access.
Ominaisuudet:
- Advanced Security Features: Many systems include encryption and anti-tampering mechanisms.
- User Management Capabilities: Easily manage multiple users and permissions.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Provides better protection against unauthorized access.
- Tarkastusketjut: Many systems log access attempts for monitoring and compliance purposes.
- Remote Management Capabilities: Administrators can modify permissions from anywhere, making it easier to manage large facilities.
Considerations:
- Power Dependency: Requires batteries or a power source; failure can lead to access issues.
- Higher Initial Cost: Usually more expensive than mechanical locks but may save money over time through reduced key management issues.
3. No Restriction Access
Overview: Some cabinets are designed without any locking mechanism, allowing unrestricted access.Sovellukset:
- Maintenance Areas: Used in situations where quick access is necessary for maintenance personnel.
- Low-Security Environments: Suitable for areas where the risk of unauthorized access is minimal.
Ominaisuudet:
- Open Access Design: No locks or keys required.
Benefits:
- Ease of Access: Quick entry for anyone who needs it.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for locking hardware.
Considerations:
- Security Risks: Provides no protection against unauthorized access, making it unsuitable for sensitive equipment.
4. Combination Electronic and Key Locking
Overview: This method combines both electronic and mechanical locking systems, offering users multiple options for securing their cabinets.
Sovellukset:
- High-Security Areas: Ideal for environments that require multiple layers of security, such as data centers or financial institutions.
- Flexible Workspaces: Useful in shared environments where different users may need varying levels of access at different times.
Ominaisuudet:
- Dual Access Options: Users can choose between electronic access and traditional keys based on their needs.
Benefits:
- Flexibility in Access Control: Allows for various methods of entry depending on circumstances.
- Backup Options Available: If the electronic lock fails, the mechanical lock still functions.
Considerations:
- Complexity in Management: Requires careful management of both keys and electronic credentials.
- Potential Higher Costs: May involve higher initial investment due to dual systems.
5. Tool Access

Overview: Tool access mechanisms allow entry using specific tools designed to open the cabinet securely.
Sovellukset
- Tool Rooms: Ideal for environments where tools need to be secured but accessed frequently by authorized personnel.
- Manufacturing Facilities: Used in settings where tools must be tracked closely to prevent loss or misuse.
Ominaisuudet
- Specialized tools required for secure opening; often includes tracking capabilities for inventory management.
Benefits
- Quick Access for Maintenance Personnel: Facilitates rapid entry during maintenance or repairs while maintaining security protocols.
Considerations
- Security Vulnerabilities: If tools are accessible to unauthorized personnel, it may compromise cabinet security.
Choosing the Right Access Restriction Method
When selecting an access restriction method for electric cabinets, buyers should consider several factors:
1. Security Needs
Assess the level of security required based on the sensitivity of the equipment housed within the cabinet. High-value or critical infrastructure components may necessitate advanced electronic locking systems with audit capabilities.
2. Environment
Consider the environmental conditions where the cabinet will be located. For instance, outdoor installations may require weather-resistant locks or latches that can withstand exposure to elements like moisture and dust.
3. User Accessibility
Evaluate how frequently authorized personnel will need to access the cabinet. For high-frequency access scenarios, electronic locks with keypad or RFID capabilities may offer convenience without compromising security.
4. Budget Constraints
Determine your budget for securing electric cabinets. Mechanical locks tend to be more cost-effective initially but may incur higher long-term costs if keys are lost or duplicated frequently. Conversely, electronic locks have higher upfront costs but can save money over time through reduced key management issues.
5. Future Scalability
Consider whether your security needs might change over time. Systems that allow easy addition or modification of user credentials can provide long-term flexibility as personnel changes occur within an organization.
Päätelmä
Choosing the right access restriction method for electric cabinets is essential for ensuring security and ease of use. By understanding the different options available—ranging from traditional key locks to advanced electronic systems—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Investing in appropriate locking mechanisms not only protects valuable assets but also enhances operational efficiency by ensuring that authorized personnel can easily access what they need when they need it. As technology evolves, staying updated on new locking mechanisms will help buyers effectively secure their investments while adapting to future security challenges. In summary, each method has its unique applications and benefits that cater to various industries and environments. Understanding these differences will empower buyers to select the most suitable access restriction method tailored to their specific requirements, ensuring both security and efficiency in managing their electric cabinets.